Experimental variogram¶
Overview¶
The experimental variogram calculation is adapted from geostatsmodels to handle both 2D and 3D cases. Results are checked against Isatis for sanity (see unit tests).
Algorithm¶
Compute 3D distances pairwaise between points in dataset
Identify pairs of points included in a lag range
Given azimuth, dip and pitch angle inputs, identify pairs belonging to an angular range (considering an input angular tolerance). Matching pairs are also selected at opposite angle (180° azimuth rotation)
The semivariance (or covariogram, depending on user’s choice) is then computed for all the lags, according to the input values of each points for all the selected pairs.
Input¶
The variogram calculations accepts the following angles in degrees:
azimuth: clockwise angle from the North on the horizontal plane, giving the strike direction
dip: angle from horizontal plane along the dipping direction (perpendicular to the strike direction)
pitch: clockwise angle from the strike direction on the dipping plane
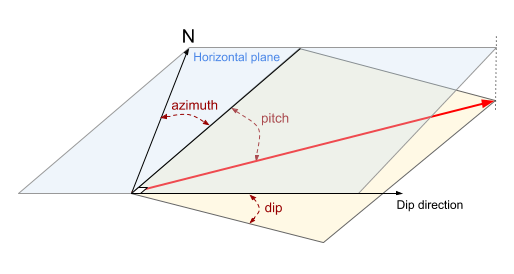
A 3D interactive tool is available to help you visualize these angles.
Angular tolerance (atol) in degrees, slicing width and slicing
height are defined as below: 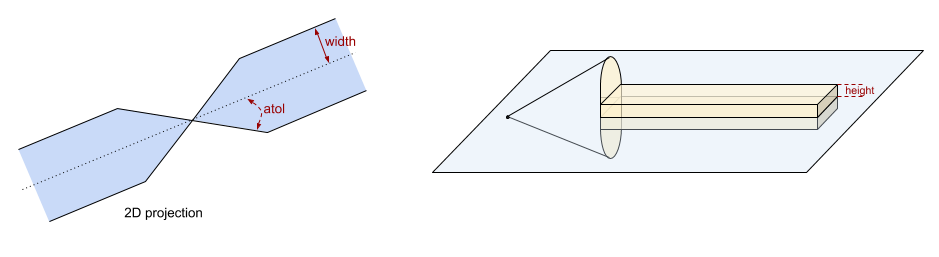
Output¶
The geolime variogram output is intended to be as close as Isatis output. A typical geolime variogram outputs:
rank npairs lag avgdist vario
0 4 1 60 57.6806 1568.000000
1 5 3 75 71.9403 2608.166667
2 6 2 90 86.3444 759.250000
3 7 1 105 105.894 32.000000
4 8 2 120 122.254 740.000000
5 9 2 135 130.186 5870.250000
6 10 2 150 151.782 900.250000
7 11 2 165 170.897 2866.250000
8 12 2 180 185.647 2358.250000
9 13 4 195 198.692 345.625000
10 14 10 210 211.139 1274.000000